The Impact Of EVs On The Global Oil Industry: A Deep Dive
October 1, 2023 | by Jacob Kang
Are you curious about how the rise of electric vehicles (EVs) is affecting the global oil industry? In our article “The Impact of EVs on the Global Oil Industry: A Deep Dive,” we examine this phenomenon and its potential ramifications. As EVs continue to gain popularity, traditional oil consumption is expected to decline, causing significant shifts in the oil market and posing challenges for the fossil fuel industry. Join us as we explore the implications of this electrifying trend and its potential impact on the future of the oil industry.
1. Introduction to EVs
1.1 What are EVs?
Electric Vehicles (EVs) are vehicles that are powered entirely or partially by electricity. They are an alternative to conventional vehicles that rely on internal combustion engines fueled by gasoline or diesel. EVs use rechargeable batteries to store electricity, which powers an electric motor to propel the vehicle. They come in various forms, including all-electric vehicles (AEVs) that run solely on electricity, and plug-in hybrid electric vehicles (PHEVs) that combine electricity and conventional fuels.
1.2 How do EVs work?
EVs work by converting electrical energy stored in batteries into mechanical energy to power the vehicle’s movement. The batteries are charged by plugging the vehicle into an electrical outlet or charging station. When driving, the electricity stored in the batteries is sent to the electric motor, which then spins the wheels and propels the vehicle forward. Some EVs also use regenerative braking, which converts kinetic energy into electrical energy and stores it back in the batteries.
1.3 History of EVs
Although EVs are gaining popularity in recent years, their history dates back to the early 19th century. The first electric-powered vehicle was developed by Thomas Davenport in 1834. However, it was not until the late 19th century that EVs gained traction, with notable advancements by inventors like Thomas Edison and Nikola Tesla. The early 20th century saw a rise in the use of gasoline-powered vehicles, which led to a decline in EVs. However, with concerns about climate change and the need for sustainable transportation, EVs have made a comeback in the 21st century.
2. Growth of EV Market
2.1 EV sales and market share
The global market for EVs has been experiencing significant growth in recent years. According to the International Energy Agency (IEA), the global electric car stock surpassed 5 million vehicles in 2018. China has emerged as the largest market for EVs, followed by Europe and the United States. The sales of EVs have been steadily increasing, driven by factors such as government incentives, declining battery costs, and the introduction of new and more affordable EV models.
2.2 Global EV adoption rates
The adoption rate of EVs varies across different regions and countries. Norway has been at the forefront of EV adoption, with electric cars accounting for a significant portion of new car sales. Other countries like the Netherlands, Sweden, and China have also witnessed a rapid increase in EV adoption. In contrast, some regions, including certain parts of the United States, are lagging in EV penetration. However, the overall trend shows a positive trajectory of increasing EV adoption worldwide.
2.3 Government incentives and policies
Government incentives and policies have played a crucial role in driving the growth of the EV market. Many countries have implemented various measures to encourage consumers to switch to electric vehicles. These include financial incentives such as tax credits, rebates, and grants, as well as non-financial benefits like access to bus lanes, free parking, and exemption from certain tolls or congestion charges. Additionally, governments have set targets and regulations to promote the production and adoption of EVs, as part of their efforts to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and combat climate change.
3. Environmental Benefits of EVs
3.1 Reduction in greenhouse gas emissions
One of the key environmental benefits of EVs is their potential to reduce greenhouse gas emissions. EVs produce zero tailpipe emissions, meaning they do not release pollutants directly into the air during operation. As a result, they have the potential to significantly reduce carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions, which are a major contributor to climate change. The extent of emission reduction depends on the source of electricity used to charge the vehicles, with renewable energy sources providing the greatest environmental benefit.
3.2 Air pollution and public health
In addition to reducing greenhouse gas emissions, EVs also have the potential to improve air quality and public health. Traditional gasoline-powered vehicles emit pollutants such as nitrogen oxides (NOx), particulate matter (PM), and volatile organic compounds (VOCs), which contribute to air pollution and have adverse health effects. By transitioning to EVs, which produce zero tailpipe emissions, the transportation sector can play a crucial role in reducing air pollution and improving the quality of the air we breathe.
3.3 Resource conservation
EVs offer opportunities for resource conservation as well. Compared to conventional vehicles, which rely on finite fossil fuel resources, EVs can be powered by renewable energy sources such as solar or wind. This reduces the dependency on fossil fuels and helps conserve natural resources. Additionally, as battery technology continues to advance, there is also the potential for the recycling and reuse of batteries, further contributing to resource conservation.
4. Disruption to the Oil Industry
4.1 Impact on crude oil demand
The widespread adoption of EVs has the potential to significantly impact the demand for crude oil, which is a primary source of fuel for transportation. As more consumers switch to EVs, the demand for gasoline and diesel will decline, leading to a decrease in the demand for crude oil. This trend could pose significant challenges for oil-producing countries and the oil industry as a whole, which heavily relies on the transportation sector for its market.
4.2 Geopolitical implications
The disruption caused by EVs to the oil industry can have far-reaching geopolitical implications. Oil-producing nations heavily depend on oil exports for revenue, and a decrease in oil demand could impact their economic stability. Countries that heavily rely on oil revenues may need to diversify their economies and reduce their dependence on oil. Furthermore, the shift towards electric transportation could also alter the balance of power among nations, as countries with significant oil reserves may lose their leverage in global geopolitics.
4.3 Shift in investment patterns
The rise of EVs is likely to lead to a shift in investment patterns within the energy sector. As the demand for oil declines, investments may shift towards renewable energy sources and technologies that support the EV ecosystem, such as battery technology and charging infrastructure. This shift in investment patterns could have implications for oil companies and traditional energy players, as they may need to adapt their business models to remain competitive in the changing energy landscape.
5. Changing Dynamics of the Energy Market
5.1 Integration of renewable energy
The growth of EVs presents an opportunity for the integration of renewable energy into the energy market. EV chargers can be powered by renewable sources such as solar and wind, enabling the transportation sector to rely on clean and sustainable energy. This integration can help reduce greenhouse gas emissions and promote the transition to a more sustainable energy system.
5.2 Battery storage and grid resilience
EVs equipped with advanced battery technology can also contribute to grid resilience. The batteries in EVs can be used to store excess electricity generated from renewable sources during periods of low demand, and then supply it back to the grid during peak demand periods. This can help balance the intermittency of renewable energy sources and improve the overall stability and reliability of the grid.
5.3 Role of EVs in decentralized energy systems
The growth of EVs has the potential to drive the development of decentralized energy systems. EV owners can become “prosumers” by generating their own electricity through solar panels and using it to charge their vehicles. This concept of energy sharing and decentralized power generation can help create a more resilient and flexible energy system, where individuals and communities have greater control over their energy supply and consumption.
6. Challenges and Opportunities for the Oil Industry
6.1 Diversification strategies
The challenges posed by the rise of EVs present opportunities for the oil industry to diversify its business and adapt to the changing energy landscape. Oil companies can explore investments in renewable energy sources, such as wind and solar, and expand their presence in the electric mobility sector by investing in EV charging infrastructure. Diversification strategies can help oil companies remain relevant and competitive in a future with increased electrification of transportation.
6.2 Evolving role of refineries
As the demand for gasoline and diesel declines with the rise of EVs, refineries may need to adapt to changing market conditions. The focus may shift towards producing alternative fuels, such as biofuels or hydrogen, which can be used in conjunction with EVs or other low-carbon transportation options. Refineries can also explore opportunities to repurpose their infrastructure and assets for other industries or energy sectors.
6.3 Potential for collaboration with EV industry
There is potential for collaboration between the oil industry and the EV industry to address common challenges and drive innovation. Oil companies can partner with EV manufacturers and other stakeholders in the EV ecosystem to develop advanced battery technologies, improve charging infrastructure, and facilitate the integration of EVs into the energy system. Collaboration can help leverage the expertise and resources of both industries to create a more sustainable and efficient transportation sector.
7. Impact on Oil-Producing Nations
7.1 Economic implications
The impact of EVs on oil-producing nations can have significant economic implications. Countries heavily reliant on oil revenues may experience a decrease in export earnings and face challenges in sustaining their national budgets. The transition away from oil-dependent economies may require diversification efforts and investments in alternative industries to mitigate the potential economic shocks caused by the decline in oil demand.
7.2 Social and political ramifications
The societal and political ramifications of the decline in oil demand can vary across different regions. In oil-producing nations, the shift towards EVs may lead to job losses and social disruptions, as the oil industry is a major employer. Governments may need to implement social safety nets and create new employment opportunities in emerging industries to support affected communities. Additionally, the geopolitical landscape may undergo changes as countries adapt to the new energy paradigm.
7.3 Transition strategies
Oil-producing nations need to develop transition strategies to navigate the changing energy landscape and minimize the negative impacts of the decline in oil demand. This may involve diversifying the economy through investments in sectors such as renewable energy, technology, and tourism. Governments can also support the development of domestic EV industries and enhance competitiveness by nurturing research and development, encouraging local manufacturing, and attracting investments.
8. Future Outlook and Predictions
8.1 EV market projections
The future of the EV market looks promising, with projections showing continued growth and increased adoption of EVs. As battery costs continue to decline, EVs are becoming more affordable and competitive with conventional vehicles. Advancements in technology, such as longer-range batteries and faster charging, will further enhance the appeal and convenience of EVs. Projections indicate that the market share of EVs will continue to expand, potentially reaching a significant portion of global vehicle sales in the coming decades.
8.2 Oil industry response and adaptation
The oil industry is likely to respond to the rise of EVs by diversifying its business and investing in new energy technologies. Oil companies have already started to make significant investments in renewable energy projects and EV charging infrastructure. They are also exploring innovative solutions to reduce carbon emissions and improve the environmental performance of their operations. The response and adaptation of the oil industry will determine its resilience and ability to remain relevant in a future with increased electrification.
8.3 Integration of EVs into energy systems
The integration of EVs into energy systems presents opportunities for a more sustainable and efficient energy future. As EV adoption continues to grow, it will be important to develop smart charging infrastructure and grid management systems that can accommodate the increased demand for electricity. Intelligent integration of EVs into the energy system can help optimize electricity generation, distribution, and consumption, leading to a more reliable and resilient energy system.
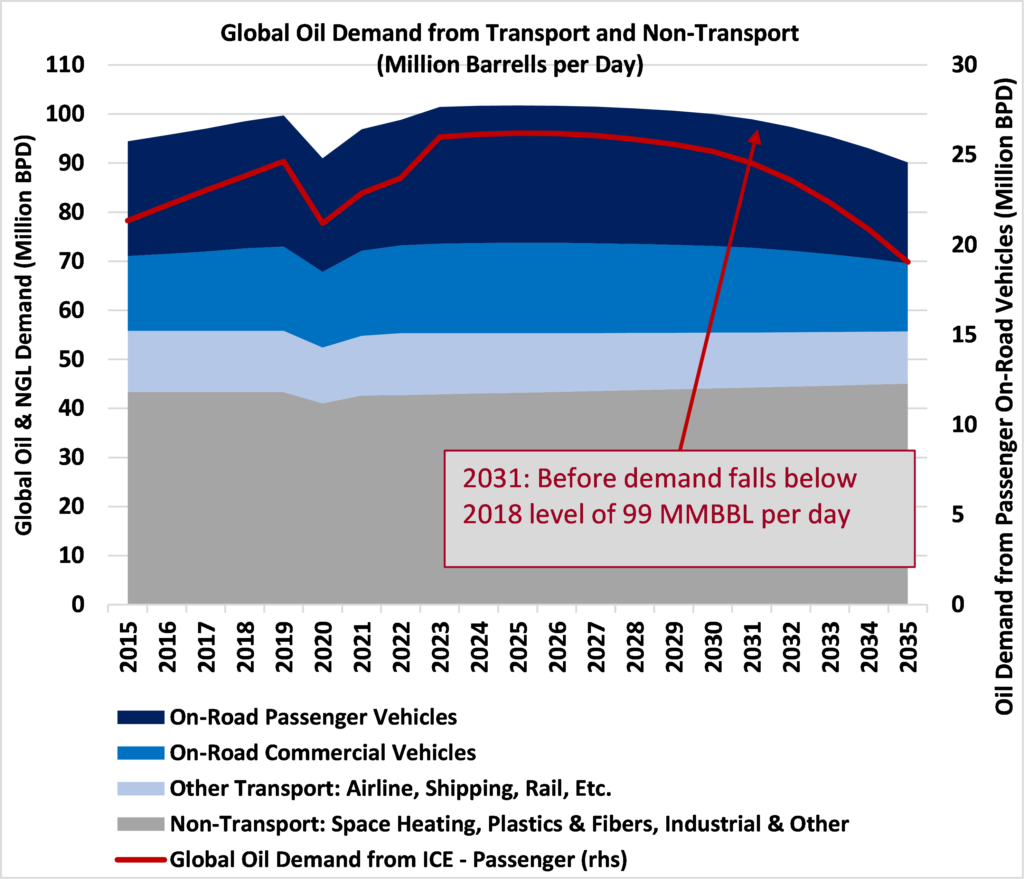
9. Conclusion
9.1 Recap of key findings
In conclusion, the impact of EVs on the global oil industry is significant and multifaceted. EVs offer environmental benefits such as reduced greenhouse gas emissions, improved air quality, and resource conservation. However, their rise also poses challenges to the oil industry, including a potential decline in crude oil demand, geopolitical implications, and a shift in investment patterns.
9.2 Implications for the global oil industry
The rise of EVs necessitates the oil industry to diversify its business and adapt to the changing energy landscape. Collaboration with the EV industry and investments in renewable energy sources can help oil companies remain competitive. Refineries may need to evolve their role and explore alternative fuel production. Oil-producing nations must develop transition strategies to mitigate the economic, social, and political disruptions caused by the decline in oil demand.
9.3 Call to action for stakeholders
Stakeholders, including governments, industries, and individuals, must actively contribute to the transition towards a sustainable transportation sector. Governments should continue to incentivize EV adoption, develop supportive policies, and invest in charging infrastructure. Industries should embrace collaboration and innovation to drive the growth of the EV ecosystem. Individuals can contribute by choosing electric vehicles, advocating for sustainable transportation, and supporting the development of renewable energy sources. Together, we can shape a future where EVs play a central role in a cleaner and more resilient energy system.
RELATED POSTS
View all


