Evaluating The Total Cost Of Ownership For EV Charger Installation
October 7, 2023 | by Jacob Kang

In this article, we will explore the topic of evaluating the total cost of ownership for EV charger installation. Installing electric vehicle chargers is becoming increasingly important as the demand for sustainable transportation continues to grow. However, it is essential to understand the overall costs involved in installing and maintaining these charging stations. By examining the various factors that contribute to the total cost of ownership, we can make informed decisions and ensure the successful implementation of EV charging infrastructure.
Choosing the Right EV Charger
When it comes to choosing an electric vehicle (EV) charger, there are several factors to consider. With the increasing popularity of electric vehicles, it is important to have a reliable and efficient EV charger that suits your needs. There are different types of EV chargers available, each with its own advantages and limitations. By understanding the types of EV chargers and considering important factors, you can make an informed decision about which charger is right for you.
Types of EV Chargers
There are three main types of EV chargers: Level 1, Level 2, and Level 3 (also known as DC fast chargers). Level 1 chargers are the most basic and typically come with the vehicle when purchased. They use a standard 120-volt outlet and provide the slowest charging speed, generally adding about 3-5 miles of range per hour of charging.
Level 2 chargers, on the other hand, use a 240-volt outlet and can charge the vehicle at a faster rate. They are commonly installed at homes and public charging stations. Level 2 chargers can add an average of 10-30 miles of range per hour of charging, depending on the vehicle’s charging capability.
Level 3 chargers are the fastest type of chargers available. They use direct current (DC) to charge the vehicle’s battery and can add about 60-80 miles of range in just 20 minutes of charging. However, Level 3 chargers are more expensive and require specialized electrical infrastructure.
When choosing an EV charger, consider your charging needs, the convenience of the charger’s location, and the compatibility with your vehicle.
Factors to Consider When Choosing an EV Charger
There are several important factors to consider when choosing an EV charger. These include:
-
Charging Speed: Determine how fast you need your vehicle to charge and choose a charger that meets your requirements.
-
Charging Port Compatibility: Ensure that the charger is compatible with the charging port of your EV. Different chargers may have different connector types.
-
Power Supply and Electrical Capacity: Consider the electrical capacity of your home or commercial property to determine if any upgrades are needed to support the charger’s power requirements.
-
Installation Space: Assess the available space for installation, both indoors and outdoors, and choose a charger that will fit comfortably in the designated area.
-
Weatherproofing and Durability: If the charger will be exposed to outdoor elements, ensure that it is weatherproof and durable to withstand different weather conditions.
-
Additional Features: Some chargers may offer additional features such as Wi-Fi connectivity, scheduling options, or smartphone apps for monitoring and controlling the charging process.
By considering these factors, you can select an EV charger that meets your specific needs and requirements.

This image is property of qmerit.com.
Cost of EV Chargers
The cost of EV chargers can vary depending on the type, brand, charging speed, and additional features. It is essential to evaluate the total cost of ownership, which includes both installation costs and operational costs over time.
Installation Costs
The installation costs of an EV charger can be significant and should be carefully considered. These costs include:
Electrical Infrastructure Upgrades
Depending on the charger’s power requirements and the existing electrical infrastructure, upgrades may be necessary to support the charger’s load. This can involve installing a dedicated circuit, upgrading electrical panels, or increasing electrical capacity.
Permitting and Inspection
Obtaining necessary permits and completing inspections to ensure compliance with local regulations can add to the installation costs. It is important to factor in these costs when planning for the installation.
Labor Costs
Professional installation by a licensed electrician is recommended to ensure safe and efficient installation. Labor costs can vary depending on the complexity of the installation and local labor rates.
Additional Equipment
In some cases, additional equipment may be required, such as electrical conduits, wiring, or mounting hardware. These additional costs should be considered when budgeting for the installation.
Site Preparation
Preparing the installation site, including any necessary excavation, concrete work, or landscaping modifications, may incur additional costs. These site preparation expenses should be taken into account when estimating the total installation costs.
Considering these different aspects of installation costs will help you determine the overall expense of installing an EV charger.
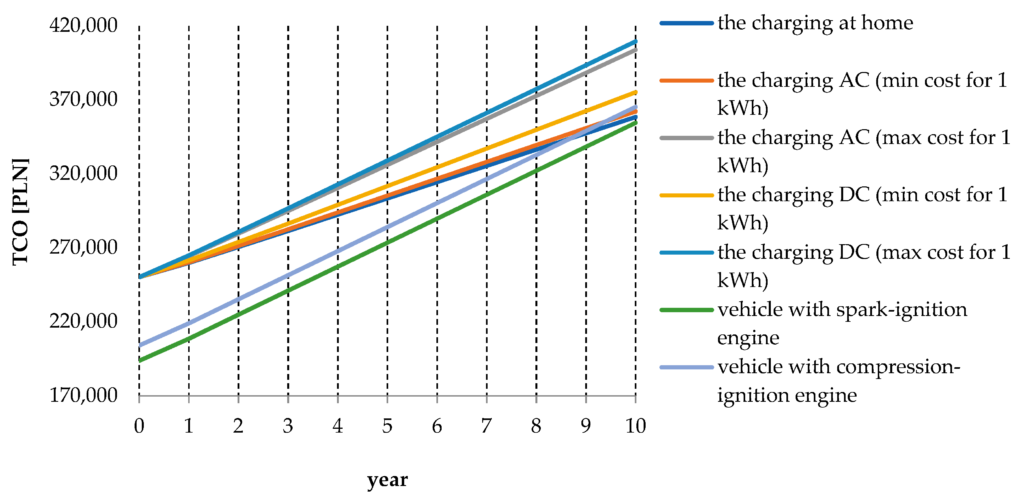
This image is property of www.mdpi.com.
Operational Costs
Beyond the initial installation costs, it is essential to consider the ongoing operational costs associated with EV chargers. These costs can include:
Electricity Costs
Charging an electric vehicle requires electricity, and the cost of electricity will contribute to the operational costs of the EV charger. It is important to check the local electricity rates and estimate the electricity consumption of the charger based on your charging needs.
Maintenance and Repairs
Like any other piece of equipment, EV chargers require regular maintenance to ensure optimal performance and longevity. Routine inspections, cleaning, and potential repairs should be factored into the operational costs.
Software and Network Subscription
Some EV chargers offer advanced software and network capabilities, which may require a subscription fee for access. These features can allow you to monitor charging sessions, manage user access, and even enable remote troubleshooting.
Insurance
It is crucial to consider insurance costs associated with the EV charger in case of any damages, accidents, or liabilities. Discussing with your insurance provider will help you determine the appropriate coverage and associated costs.
By evaluating these operational costs, you can gain a better understanding of the long-term expenses of owning an EV charger.
Financial Incentives
To encourage the adoption of electric vehicles and the installation of EV chargers, several financial incentives are available to offset the costs. These incentives can help reduce the initial investment and make the installation more affordable. Some of the common financial incentives include:
Federal Tax Credits
The U.S. federal government offers a tax credit for residential and commercial EV charger installations. The tax credit amount varies depending on the charger type and other factors. Consult with a tax professional or visit the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) website for the most up-to-date information.
State and Local Incentives
Many states and local governments provide additional incentives such as rebates, grants, or tax credits for EV charger installations. These incentives can vary by location, so it is essential to research the available programs in your area.
Utility Programs
Utility companies often offer special programs or incentives to encourage the installation of EV chargers. These programs may include discounted electricity rates during off-peak hours or utility rebates for charger installations.
Rebates and Grants
Various organizations, foundations, and non-profit entities provide rebates and grants to support EV charger installations. These incentives can help offset a portion of the installation costs and make the investment more financially viable.
By exploring these financial incentives, you can potentially reduce the overall cost of installing an EV charger.
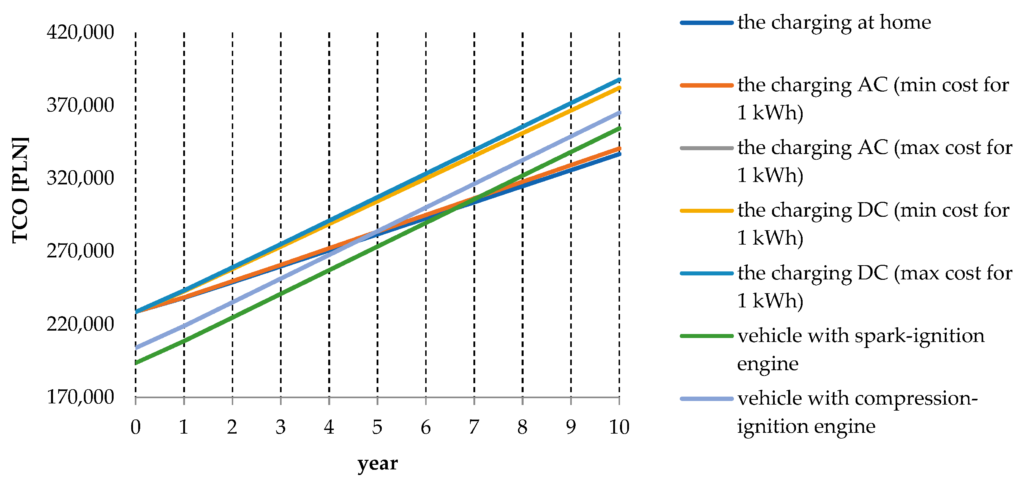
This image is property of www.mdpi.com.
Return on Investment Analysis
To evaluate the financial feasibility of installing an EV charger, conducting a return on investment (ROI) analysis is crucial. This analysis helps estimate the time it takes to recover the initial investment through savings and potential income generated by the charger. Some important metrics to consider in an ROI analysis include:
Calculating the ROI
Calculate the ROI by dividing the net profit generated by the charger over its lifetime by the initial investment. This calculation provides an estimate of the return as a percentage.
Payback Period
The payback period represents the time it takes for the charger’s net profit to equal the initial investment. A shorter payback period indicates a quicker return on investment.
Cash Flow Analysis
Analyzing the cash flow associated with the EV charger installation helps understand the financial impact over time. It considers incoming revenue from charging sessions and outgoing expenses such as electricity costs and maintenance.
Sensitivity Analysis
Performing a sensitivity analysis allows you to assess the impact of changing variables on the overall ROI. It helps identify the factors that significantly affect the financial viability of the installation.
By conducting a comprehensive ROI analysis, you can make an informed decision about the financial feasibility of installing an EV charger.
Public and Private Funding Options
In addition to the financial incentives mentioned earlier, there are other funding options available to support EV charger installations. These options include:
Grants and Loans
Various government agencies and private organizations offer grants and loans specifically for EV charger installations. These funding sources can help cover a portion or the entire installation costs, depending on the eligibility requirements.
Power Purchase Agreements (PPAs)
Under a PPA, a third-party company owns and maintains the EV charger, while you purchase the electricity generated by the charger at a predetermined rate. This allows you to avoid the upfront costs of the charger installation while still benefiting from the charging infrastructure.
Leasing Options
Some companies offer leasing options for EV chargers, allowing you to pay a monthly fee instead of purchasing the charger outright. Leasing can provide flexibility and lower upfront costs, making it a more affordable option for some individuals or businesses.
Considering these funding options can provide additional financial support and make the installation of an EV charger more accessible.
This image is property of www.mdpi.com.
Charging Infrastructure Management
Managing EV charging infrastructure involves various aspects, including software, networking, monitoring, and energy management. These elements ensure the smooth operation and efficient use of the charging infrastructure. Some key considerations for charging infrastructure management include:
Software and Network Costs
Advanced EV chargers often require software and networking capabilities to enable features like user management, data monitoring, and remote troubleshooting. These features can incur additional costs, such as subscription fees or one-time licensing fees.
System Monitoring and Maintenance
Regular monitoring and maintenance of the charging infrastructure are essential to ensure optimal performance and timely repairs. Monitoring software can provide real-time data on charging sessions, energy usage, and potential issues, while maintenance schedules help prevent breakdowns and extend the lifespan of the chargers.
Energy Management Solutions
Energy management solutions can help optimize the charging infrastructure’s energy consumption and costs. Smart charging algorithms, load balancing, and demand response programs can ensure efficient utilization of available power resources.
Demand Response Programs
Participating in demand response programs can provide financial incentives for adjusting charging schedules to align with periods of low electricity demand. By strategically managing charging sessions, you can contribute to grid stability and potentially earn credits or monetary rewards.
By implementing effective charging infrastructure management practices, you can maximize the efficiency and reliability of your EV charging infrastructure.
Scalability and Future Expansion
When planning for an EV charger installation, it is important to consider scalability and future expansion. As the demand for EVs grows and technology evolves, ensuring that the charging infrastructure can accommodate future needs becomes crucial. Some key aspects to consider for scalability and future expansion include:
Planning for Future Growth
Estimate the anticipated growth in electric vehicle adoption and plan your charging infrastructure accordingly. Consider factors such as the number of charging ports, power capacity, and space availability when designing the infrastructure.
Modularity and Flexibility
Choose EV chargers and charging infrastructure that allow for easy scalability and flexibility. Modularity enables adding or removing charging ports as needed, while flexible installation options provide the opportunity to expand the infrastructure without significant disruptions.
Upgrading and Expanding Charging Infrastructure
Consider the potential costs and requirements for upgrading or expanding the charging infrastructure in the future. Upgrading to faster chargers, increasing power capacity, or adding additional chargers may be necessary to meet evolving needs.
By being proactive in planning for scalability and future expansion, you can save time and costs associated with retrofitting or replacing the charging infrastructure down the line.

This image is property of admin.energy5.com.
Lifecycle Assessment
Understanding the environmental impact of EV chargers and considering end-of-life considerations is an important aspect of responsible and sustainable installation. Conducting a lifecycle assessment helps evaluate the charger’s environmental footprint throughout its life cycle. Some important considerations in a lifecycle assessment include:
Environmental Impact of EV Chargers
Consider the materials used in the charger’s construction, energy consumption during manufacturing, operational emissions, and potential impact on natural resources. Choosing chargers that incorporate sustainable materials and utilize renewable energy sources can help minimize environmental impact.
End-of-Life Considerations
Evaluate the charger’s recycling potential and the proper disposal of components at the end of their life. Understanding the options for recycling or repurposing the charger’s components can contribute to a more circular economy and reduce electronic waste.
Sustainability and Circular Economy
Consider chargers that are designed with sustainability in mind. Look for chargers manufactured using environmentally friendly practices, with a focus on minimizing waste, maximizing recycling, and reducing carbon emissions.
By considering the lifecycle of an EV charger and its impact on the environment, you can make more environmentally conscious decisions throughout the installation process.
Case Studies
Examining successful EV charger installations and learning from real-world experiences can provide valuable insights. Case studies showcase the challenges faced, lessons learned, and best practices for a successful EV charger installation. By reviewing case studies, you can gain practical knowledge and apply it to your own installation.
Successful EV Charger Installations
Case studies can highlight successful EV charger installations in various settings, such as residential, commercial, or public locations. These studies may provide information on the charging infrastructure design, installation process, operational challenges, and user experiences.
Lessons Learned
By reviewing lessons learned from previous installations, you can avoid common pitfalls and make informed decisions. Case studies often touch on challenges, unexpected costs, or technical issues that arose during the installation and operation of the chargers, allowing you to plan accordingly.
Learning from the experiences of others can help ensure a smooth and successful installation of your own EV chargers.
In conclusion, choosing the right EV charger involves considering various factors, including charger types, installation costs, operational costs, financial incentives, return on investment analysis, funding options, infrastructure management, scalability, lifecycle assessment, and lessons learned from case studies. By thoroughly evaluating these aspects, you can make an informed decision about the most suitable EV charger for your needs and budget. Remember, installing an EV charger not only benefits you but also contributes to a greener future by promoting the use of clean energy and reducing carbon emissions.
RELATED POSTS
View all

