EV Chargers: A Key Component Of The Electric Vehicle Ecosystem
October 22, 2023 | by Jacob Kang

If you’ve ever wondered how electric vehicles are powering up, look no further than EV chargers. These unassuming devices are the unsung heroes of the electric vehicle ecosystem, providing the vital connection between EVs and their power source. In this article, we’ll explore the importance of EV chargers and their role in supporting the widespread adoption of electric vehicles. From the different types of chargers available to the benefits of owning one, we’ll dive into all things EV charger-related, shedding light on why they are a key component of the electric vehicle revolution. So, buckle up and get ready to plug into the world of EV chargers.
The Growing Electric Vehicle Market
electric vehicles (EVs) have gained significant popularity in recent years, with increasing adoption by consumers around the world. This growing market can be attributed to several factors, including the increasing awareness of environmental issues, improvements in battery technology, and government incentives. As the number of EVs on the road continues to rise, the need for a robust charging infrastructure becomes crucial. In this article, we will explore the different types of EV chargers, their characteristics and features, the installation process, as well as the benefits and challenges associated with EV charging. We will also discuss government initiatives and incentives, emerging technologies, and the future outlook of the EV charging market.

Increasing Adoption of Electric Vehicles
The adoption of electric vehicles has been steadily increasing over the past few years. With advancements in battery technology, EVs offer longer ranges and improved performance, which has sparked the interest of consumers. Additionally, EVs produce zero tailpipe emissions, making them a more environmentally friendly alternative to traditional internal combustion engine vehicles. As more people become aware of the advantages of driving electric, the demand for EVs continues to grow.
Need for a Robust Charging Infrastructure
One of the key challenges in the widespread adoption of electric vehicles is the need for a robust charging infrastructure. Unlike conventional gasoline-powered vehicles, EVs require access to charging stations to recharge their batteries. Having an extensive network of chargers is essential to eliminate range anxiety and ensure that EV owners have convenient access to charging facilities wherever they go. A reliable and widespread charging infrastructure is crucial to support the growing number of EVs on the road.
Significance of EV Chargers in the Ecosystem
EV chargers play a crucial role in the electric vehicle ecosystem. They act as the lifeline for EVs, providing the necessary power to recharge their batteries. Without a sufficient number of chargers, EVs would be limited in their range and usability, making them less appealing to consumers. EV chargers enable EV owners to travel longer distances and provide the convenience of recharging at home, work, or while running errands. Additionally, the availability and accessibility of chargers contribute to reducing the dependency on fossil fuels and promoting the use of clean energy sources.
Types of EV Chargers
There are several types of EV chargers available, each offering different charging speeds and capabilities. Understanding the different types of chargers is essential for both EV owners and those involved in the charging infrastructure development.
Level 1 chargers
Level 1 chargers are the most basic type of EV chargers and are commonly referred to as “trickle chargers.” These chargers typically come with the vehicle and are designed to be plugged into a standard household outlet. While they are convenient for overnight charging, they have the slowest charging speeds, making them less suitable for rapid recharging needs.
Level 2 chargers
Level 2 chargers offer faster charging speeds compared to Level 1 chargers. They require a dedicated 240-volt circuit and are typically installed at home, workplaces, or public charging stations. Level 2 chargers can provide charging rates of 10-60 miles of range per hour, depending on the EV’s battery capacity and the charger’s power output. These chargers are ideal for overnight charging or when the vehicle is parked for an extended period.
DC fast chargers
DC fast chargers, also known as Level 3 chargers, are designed to provide a rapid charging experience for EV owners. These chargers operate at higher voltages and can deliver charging rates of up to 80% capacity in as little as 20-30 minutes, depending on the EV model and battery size. DC fast chargers are commonly found along major highways, enabling long-distance travel for EV owners.
Wireless charging technology
Wireless charging technology is an emerging trend in the EV charging market. This technology eliminates the need for physical connectors and allows for convenient charging by simply parking over a charging pad. Wireless chargers use electromagnetic fields to transfer energy between the charging pad and the vehicle. While still in the early stages of development, wireless charging has the potential to revolutionize the EV charging experience, providing even greater convenience and ease of use for EV owners.
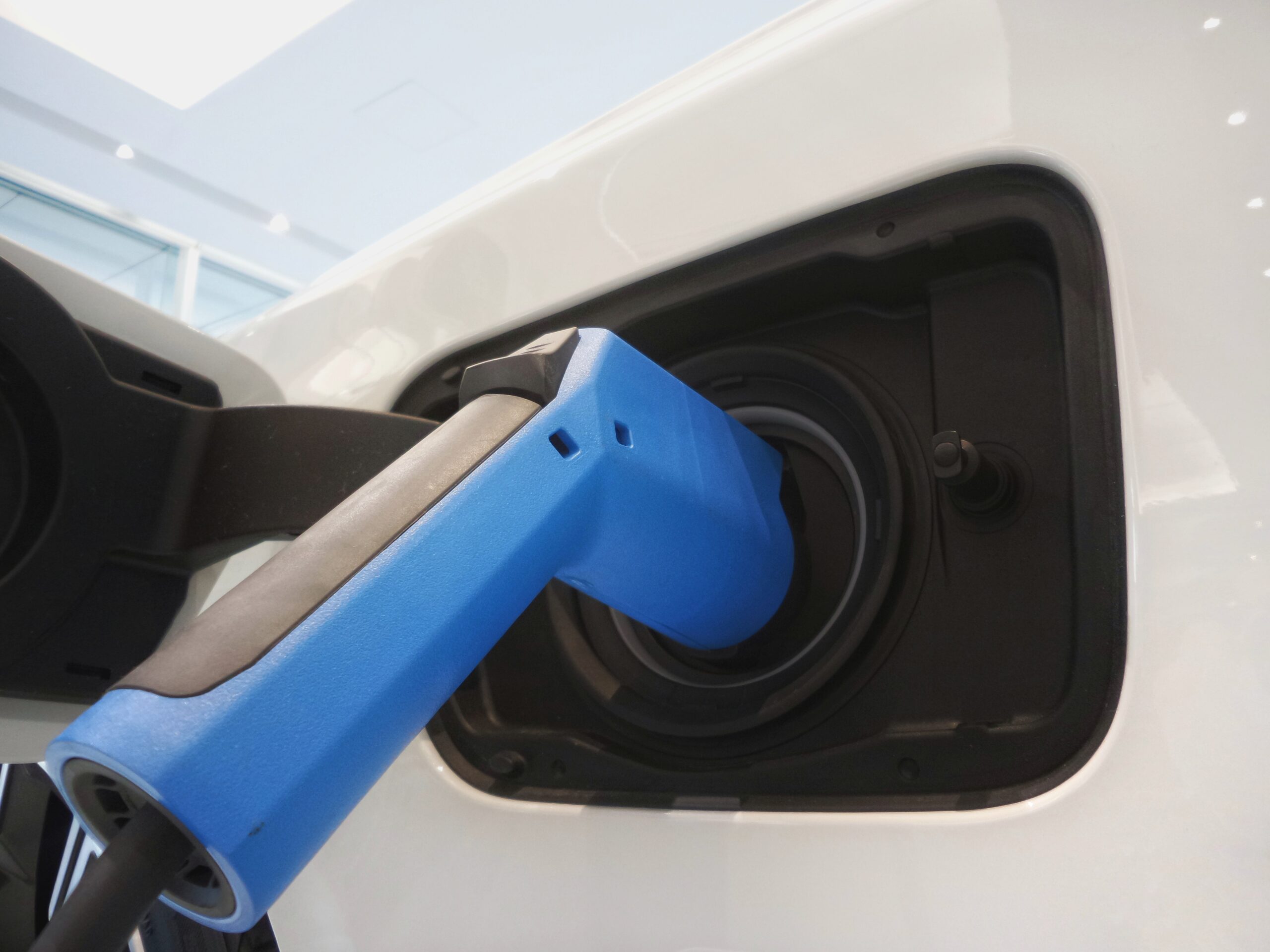

Characteristics and Features of EV Chargers
When choosing an EV charger, there are several characteristics and features to consider. These factors can impact the charging speed, compatibility, safety, and integration with renewable energy sources.
Power Output and Charging Speed
The power output of an EV charger determines the charging speed. Higher power outputs result in faster charging times, allowing EV owners to quickly recharge their vehicles. Different chargers offer various power outputs, ranging from a few kilowatts for Level 1 chargers to several hundred kilowatts for DC fast chargers. It is important to consider the desired charging speed and choose a charger with an appropriate power output based on individual needs.
Connector Types and Compatibility
Different EV models use varying connector types for charging. The two main types are the J1772 connector, commonly used for Level 1 and Level 2 charging, and the CCS (Combined Charging System) connector, predominantly used for DC fast charging. It is essential to ensure that the chosen charger supports the appropriate connector type for the EV model to ensure compatibility and proper charging.
Smart Charging Capabilities
Smart charging capabilities allow EV owners to optimize their charging experience and reduce energy costs. These features enable users to schedule charging sessions during off-peak hours when electricity rates are lower. Additionally, some chargers offer smartphone applications that allow remote monitoring and control of the charging process. Smart charging capabilities enhance the convenience and flexibility for EV owners, making it easier to manage their charging needs.
Safety Features
Safety is of utmost importance when it comes to EV chargers. Chargers should have built-in safety features such as overcurrent protection, ground fault protection, and overheating prevention mechanisms. These features ensure the safe and reliable operation of the charger, protecting both the vehicle and the user. Third-party certifications, such as UL certification, give additional assurance of the charger’s safety and reliability.
Integration with Renewable Energy Sources
Many EV owners are environmentally conscious and strive to minimize their carbon footprint. Integrating EV chargers with renewable energy sources, such as solar panels or wind turbines, allows for greener and more sustainable charging. This integration enables EV owners to charge their vehicles using clean energy, further reducing their environmental impact.
EV Charger Installation
EV chargers can be installed in various locations to cater to different charging needs. The installation process may vary depending on the location and type of charger.
Residential Charging Stations
Residential charging stations are typically installed in the owner’s garage or driveway. These chargers provide a convenient and reliable charging solution for EV owners, allowing them to conveniently charge their vehicles overnight. The installation process typically requires a licensed electrician to ensure the charger is safely and correctly connected to the home’s electrical system.
Public Charging Infrastructure
Public charging infrastructure plays a vital role in supporting EV adoption and enabling long-distance travel. These chargers are usually located in public parking lots, shopping centers, and along major roadways. The installation of public charging infrastructure requires careful planning to determine the suitable locations and to ensure proper electrical connections and accessibility for users.
Workplace Charging Stations
Workplace charging stations offer a convenient charging solution for employees who spend a significant amount of time at their workplace. These chargers are typically installed in employee parking lots or garages, providing EV owners with the opportunity to charge their vehicles during their workday. Installing workplace charging stations can be beneficial for companies as it promotes sustainable transportation options and encourages employee retention.
Integration with Parking Facilities
Integrating EV chargers with parking facilities, such as parking garages or parking lots, allows EV owners to charge their vehicles while they are away. This integration enables EV owners to take advantage of their parking time by replenishing their battery levels, ensuring they have a fully charged vehicle when they return to their car. Installing chargers in parking facilities requires careful planning and coordination to optimize the usage of charging spots and facilitate a seamless charging experience for users.
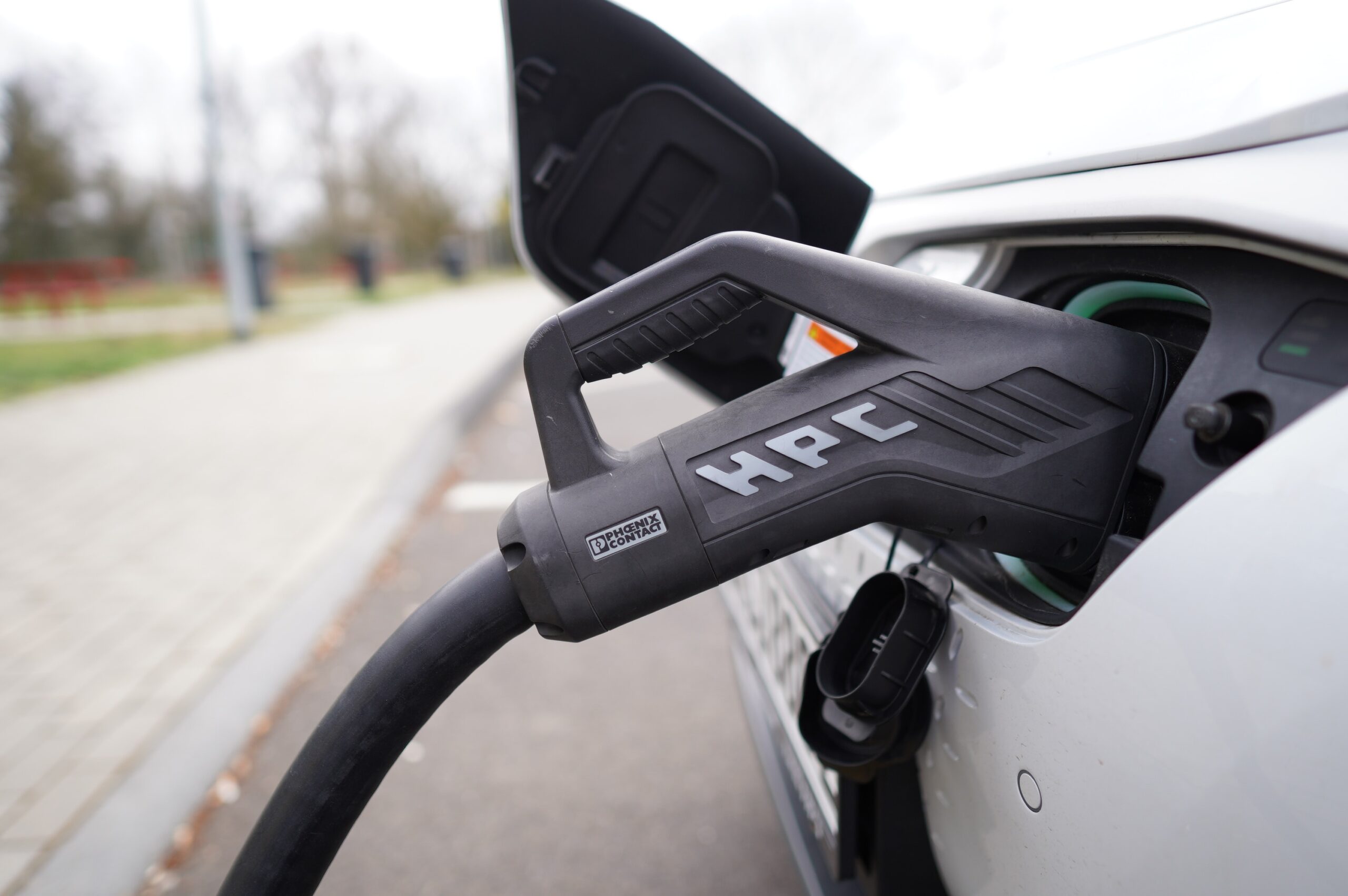

Benefits of EV Chargers
EV chargers offer numerous benefits to EV owners, the environment, and the entire energy grid.
Convenience and Flexibility for EV Owners
Having access to convenient charging stations provides EV owners with the flexibility to charge their vehicles whenever and wherever they need to. Whether it’s at home, work, or during a road trip, a reliable charging infrastructure ensures that EV owners can easily recharge their vehicles and enjoy the benefits of electric transportation without any major inconveniences.
Environmental Advantages
One of the key advantages of EVs is their significant reduction in greenhouse gas emissions compared to traditional gasoline-powered vehicles. By charging EVs using renewable energy sources, such as solar or wind power, the environmental benefits are further amplified, resulting in even lower carbon emissions and a cleaner air quality.
Reduced Dependency on Fossil Fuels
EVs offer an opportunity to reduce the dependency on fossil fuels, which are finite and contribute to various environmental problems, including air pollution and climate change. With an efficient and widespread charging infrastructure, EV owners can rely less on gasoline and transition to a more sustainable and renewable energy source.
Potential for Cost Savings
Charging an electric vehicle typically costs less than refueling a gasoline-powered vehicle. Electricity prices are generally lower than gasoline prices, and some regions offer discounted rates for EV charging during off-peak hours. Additionally, EV owners can save on maintenance costs, as electric vehicles have fewer moving parts and require less regular maintenance compared to traditional vehicles.
Positive Impact on the Grid
Managed charging and vehicle-to-grid (V2G) integration can play a significant role in supporting the stability and reliability of the energy grid. Through smart charging and V2G technologies, EVs can act as grid resources, helping to balance electricity demand and supply, and facilitating the integration of renewable energy sources into the grid. This symbiotic relationship between EVs and the grid can contribute to a more sustainable and resilient energy system.
Challenges and Roadblocks in EV Charging
While the EV charging market has witnessed significant growth, there are still challenges and roadblocks that need to be addressed to overcome potential barriers to widespread adoption.
Limited Charging Infrastructure
One of the major challenges is the limited availability of charging infrastructure, especially in certain regions or remote areas. The installation of charging stations requires significant investment and coordination between various stakeholders, including governments, utility companies, and private entities. Expanding the charging infrastructure to ensure broad coverage and accessibility remains a key priority to support the continued growth of the EV market.
Range Anxiety and Long Charging Times
Range anxiety, the fear of running out of battery while driving, is a common concern among potential EV owners. Although the range of EVs has improved, it is still lower compared to internal combustion engine vehicles. This, coupled with longer charging times for certain types of chargers, can deter some consumers from switching to electric. Increasing the availability and accessibility of fast-charging stations can help alleviate range anxiety and make EVs a more viable option for long-distance travel.
Cost Implications for Installation
The cost of installing EV charging infrastructure can be a significant barrier for individuals and businesses. The installation of chargers often requires electrical upgrades, dedicated circuits, and sometimes even significant construction work. The associated costs can vary depending on the location, type of charger, and electrical requirements, making it challenging for some stakeholders to invest in the necessary infrastructure. Governments and utility companies can play a crucial role in providing incentives and financial support to reduce the upfront costs and promote the installation of chargers.
Standardization and Interoperability Issues
Standardization and interoperability of charging equipment and connector types remain an ongoing challenge in the EV charging market. Different regions and manufacturers have adopted various standards and protocols, resulting in a fragmented charging ecosystem. This lack of standardization can create confusion for EV owners and hinder the seamless interoperability between chargers and vehicles. An industry-wide effort to establish common standards and protocols is crucial to ensure compatibility and ease of use for EV owners.

Government Initiatives and Incentives
To support the growth of the EV market and the development of charging infrastructure, governments around the world have implemented various initiatives and incentives.
Investments in Charging Infrastructure
Many governments are investing in the development of charging infrastructure to expand the network of chargers. These investments aim to increase the availability and accessibility of charging stations, especially in public spaces and along major transportation routes. Governments are collaborating with utility companies, private entities, and other stakeholders to ensure the effective deployment of charging infrastructure to meet the demands of the growing EV market.
Subsidies and Grants for EV Charger Installation
To encourage the installation of EV chargers, governments offer subsidies and grants to individuals and businesses. These incentives help offset the initial costs associated with charger installation, making it more financially feasible for stakeholders. By providing financial support, governments aim to accelerate the deployment of charging infrastructure and promote the adoption of electric vehicles.
Regulatory Frameworks and Policies
Regulatory frameworks and policies play a critical role in shaping the EV charging market. Governments are implementing regulations and standards to ensure the safety, reliability, and interoperability of charging infrastructure. They are also developing policies to promote the use of renewable energy sources for charging, encourage the installation of chargers in new or existing buildings, and facilitate the expansion of public charging infrastructure. These regulatory measures aim to create a favorable environment for the growth and sustainability of the EV charging market.
Collaboration with the Private Sector
Governments are collaborating with the private sector to leverage expertise, resources, and investments in the EV charging ecosystem. Public-private partnerships are being formed to develop innovative solutions, streamline the installation process, and ensure the effective operation and maintenance of charging infrastructure. The collaboration between governments and the private sector is crucial to address the challenges in the EV charging market and drive the transition towards a cleaner and more sustainable transportation system.
Emerging Technologies and Innovations
The EV charging market is continuously evolving, with several emerging technologies and innovations that have the potential to transform the charging experience and enhance the integration of electric vehicles into the energy ecosystem.
Ultra-Fast Charging Advancements
Advancements in charging technology are enabling ultra-fast charging capabilities. By increasing the power output and utilizing advanced charging algorithms, chargers can deliver even faster charging times. Ultra-fast charging enables EV owners to recharge their vehicles in a matter of minutes, making long-distance travel more convenient and practical.
Vehicle-to-Grid (V2G) Integration
Vehicle-to-grid (V2G) integration allows EVs to function as energy storage devices and feed electricity back into the grid when needed. This bidirectional flow of electricity enables EVs to act as mobile batteries, helping balance the grid’s electricity demand and supply. V2G integration has the potential to provide flexibility to the grid, support renewable energy integration, and create new revenue streams for EV owners.
Inductive Charging Systems
Inductive charging systems, also known as wireless charging, offer a cable-free and effortless charging experience. These systems use magnetic fields to transfer energy from the charging pad to the vehicle’s receiver pad. Inductive charging eliminates the need for physical connectors, making charging as simple as parking the vehicle over a charging pad. Although still in the early stages of development, inductive charging systems have the potential to enhance the convenience and ease of use of EV chargers.
Battery Swapping Solutions
Battery swapping is another emerging technology that aims to address the issue of long charging times. Instead of waiting for the battery to charge, EV owners can simply swap their depleted battery with a fully charged one at a battery swapping station. This approach significantly reduces charging times and allows for continuous usage of the vehicle. Battery swapping has the potential to make EVs more comparable to traditional gasoline-powered vehicles in terms of refueling time.

Future Outlook and Market Trends
The future of the EV charging market looks promising, with several market trends and developments set to shape the industry.
Rapidly Expanding Charging Network
The charging network is expected to grow rapidly in the coming years to meet the increasing demand for EV charging. Governments, utility companies, and private entities are actively investing in the deployment of charging infrastructure, aiming to achieve broad coverage and accessibility. The expansion of the charging network will make EV ownership and usage more convenient, contributing to further market growth.
Increased Deployment of DC Fast Chargers
DC fast chargers are predicted to become more prevalent, especially along major highways and high-traffic areas. The capability of DC fast chargers to recharge vehicles rapidly makes them essential for enabling long-distance travel and reducing range anxiety. As battery technology continues to improve, the deployment of DC fast chargers will play a crucial role in supporting the future of electric mobility.
Integration with Smart Grid Systems
The integration of EV charging infrastructure with smart grid systems holds great potential for optimizing electricity demand and supply. Smart charging algorithms and V2G integration can enable EVs to participate in demand response programs, helping balance the grid and improve the utilization of renewable energy sources. This integration will result in a more efficient energy ecosystem and pave the way for a sustainable and intelligent energy grid.
Advancement in Battery Technology
Battery technology is a key driver in the EV market, and further advancements are anticipated in the coming years. R&D efforts are focused on increasing battery energy density, reducing costs, and improving charging performance. These advancements will result in EVs with longer ranges, shorter charging times, and increased affordability, making electric vehicles an even more attractive option for consumers.
Conclusion
EV chargers are a key component of the electric vehicle ecosystem and play a vital role in supporting the widespread adoption of electric vehicles. With increasing adoption of EVs, the need for a robust charging infrastructure becomes imperative. Level 1 chargers, Level 2 chargers, DC fast chargers, and wireless charging technology offer different charging speeds and capabilities to accommodate various charging needs. Characteristics and features such as power output, connector types, smart charging capabilities, safety features, and integration with renewable energy sources are essential considerations when choosing an EV charger. Installation of chargers can be done at residential locations, public spaces, workplaces, and parking facilities, expanding the accessibility of charging stations. EV chargers offer numerous benefits, including convenience, environmental advantages, reduced dependency on fossil fuels, potential cost savings, and a positive impact on the grid. However, challenges such as limited charging infrastructure, range anxiety, installation costs, and standardization issues need to be addressed. Governments are implementing initiatives and incentives to promote the growth of the EV charging market, investing in charging infrastructure, offering subsidies, and developing regulatory frameworks. Emerging technologies, including ultra-fast charging, vehicle-to-grid integration, inductive charging systems, and battery swapping, are set to revolutionize the EV charging experience. The future of the EV charging market looks promising, with a rapidly expanding charging network, increased deployment of DC fast chargers, integration with smart grid systems, and advancements in battery technology. As the electric vehicle market continues to evolve, the development of a robust charging infrastructure is essential to drive the transition towards cleaner and more sustainable transportation.
RELATED POSTS
View all